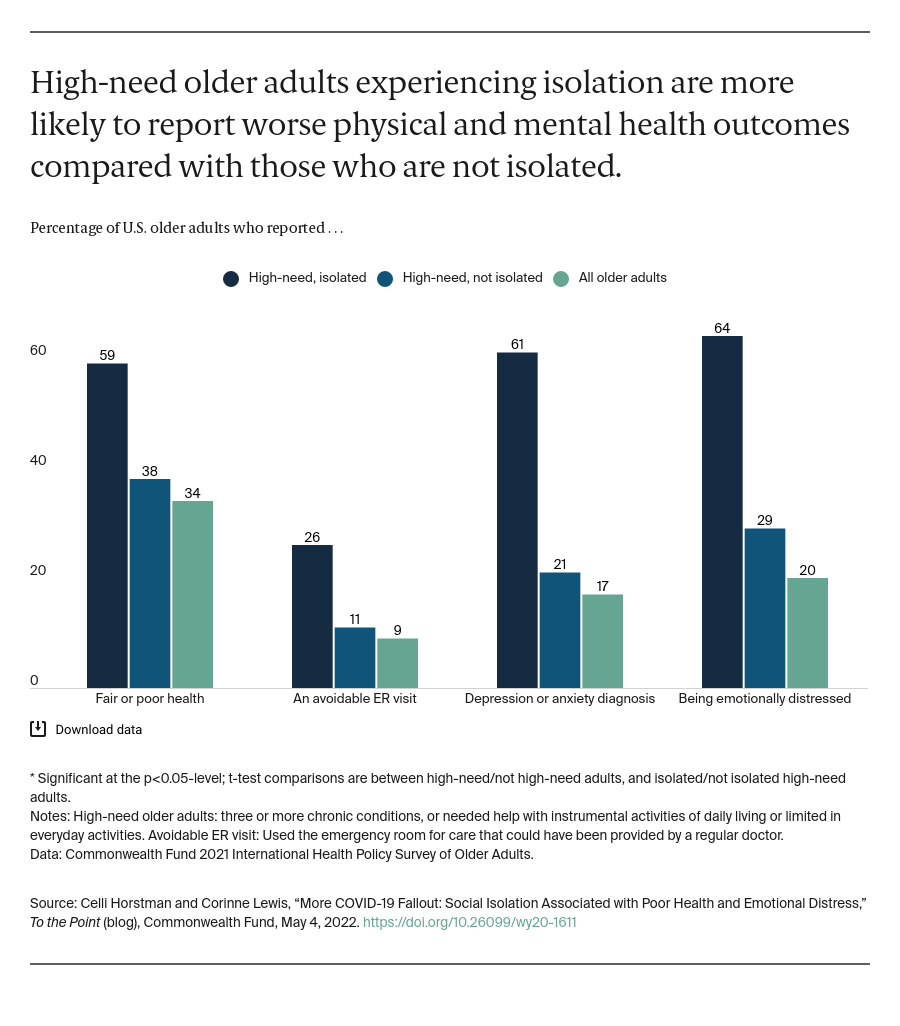
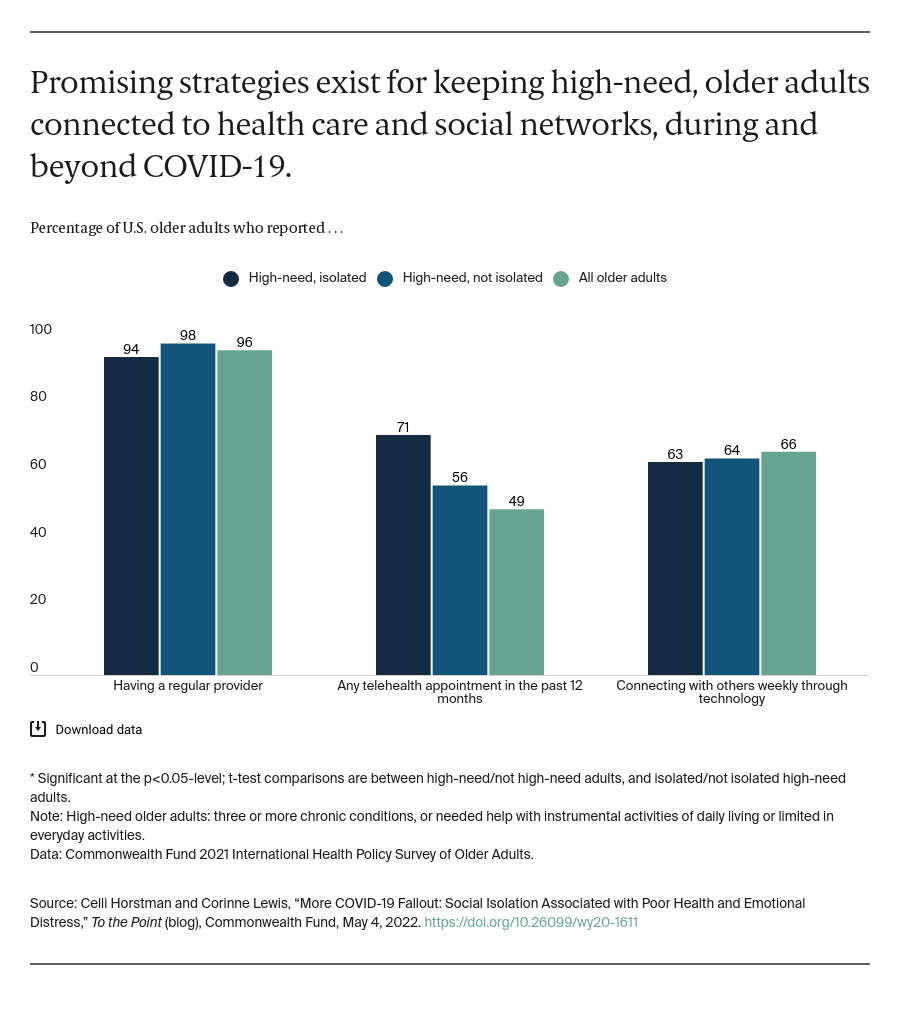
As a result of social distancing and other interventions, the COVID-19 pandemic has cut many people off from their emotional and social support systems. For older adults, this may have exacerbated feelings of isolation; the percentage of those who reported feeling isolated jumped from 27 percent in 2018 to 56 percent after the start of the pandemic. This is particularly concerning for older adults with high health care needs — that is, people with multiple chronic conditions or functional limitations who require assistance with daily activities. Feelings of isolation not only create emotional distress but also have the potential to further exacerbate their already complicated health problems and even contribute to early mortality. Social distancing was an effective approach to slowing COVID-19 transmission — especially among a population at increased risk of infection — but any resulting feelings of isolation may have contributed to new health and social risks for this medically vulnerable group.
To explore how isolation affects high-need older adults and examine their experiences during the pandemic, we analyzed data from the Commonwealth Fund 2021 International Health Policy Survey of Older Adults. We found, consistent with previous research, that high-need adults are significantly more likely to report social isolation; more than one of 10 (12%) high-need older adults reported often feeling isolated from others, compared to 5 percent of older adults without high needs.