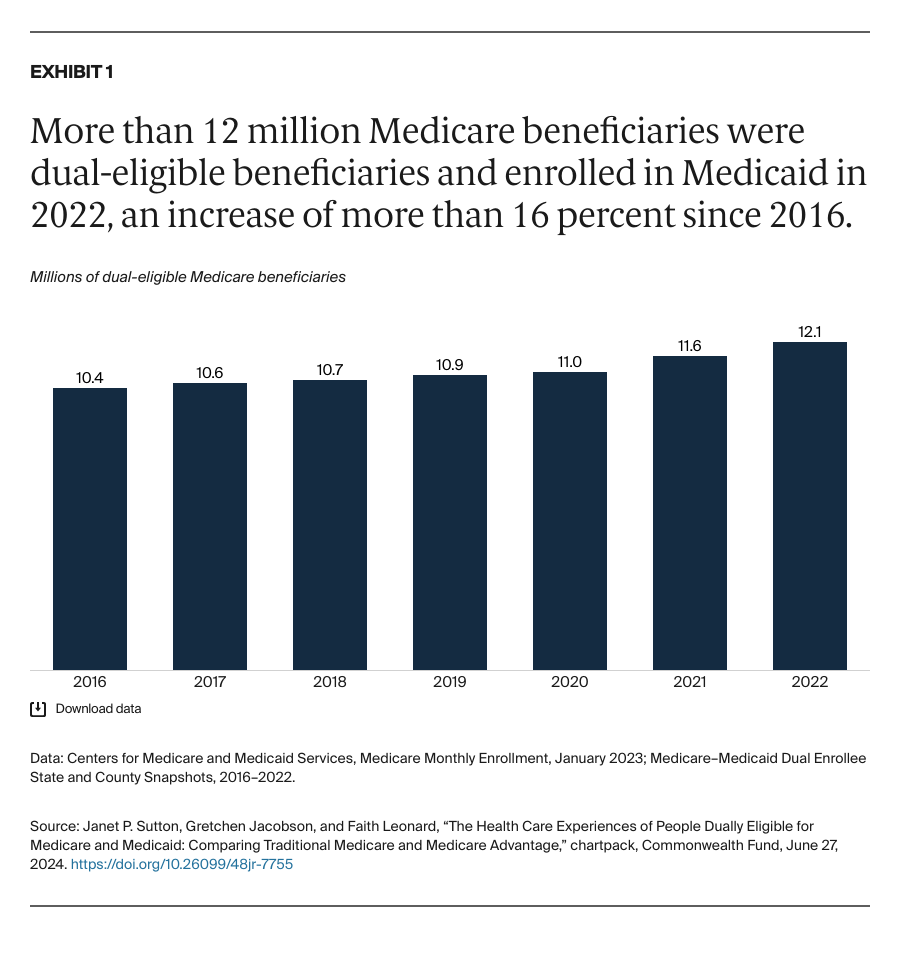
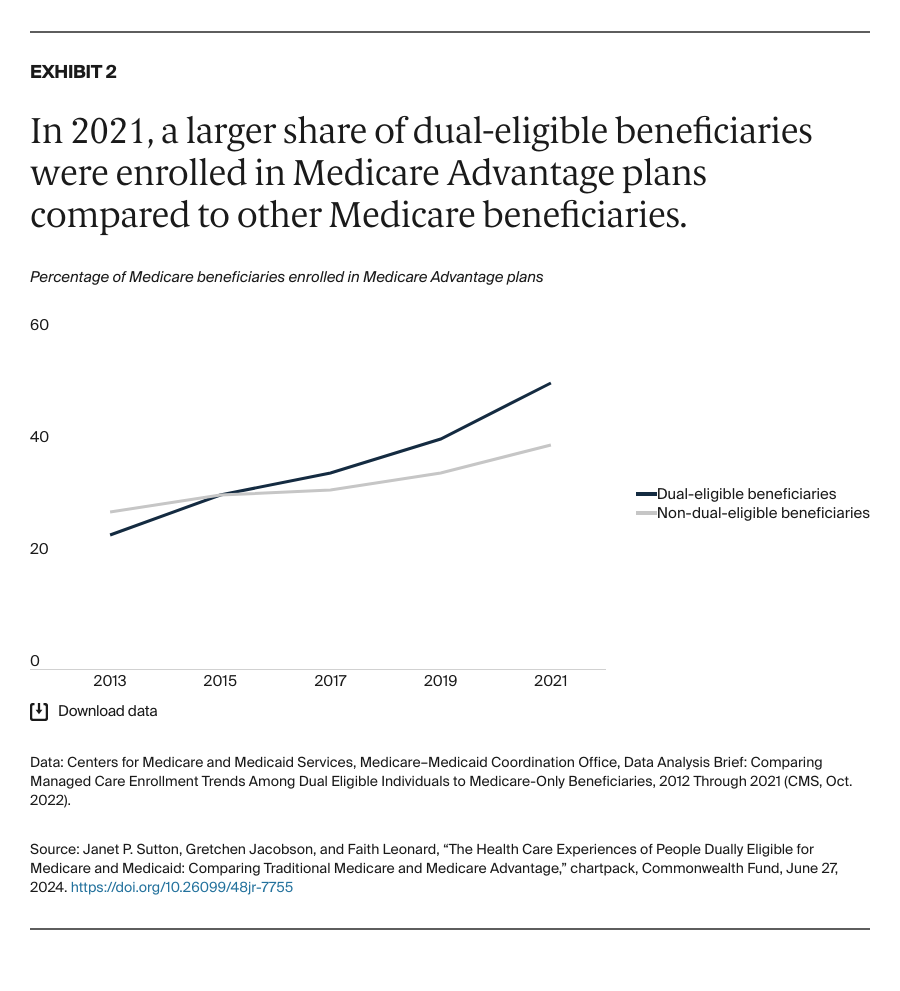
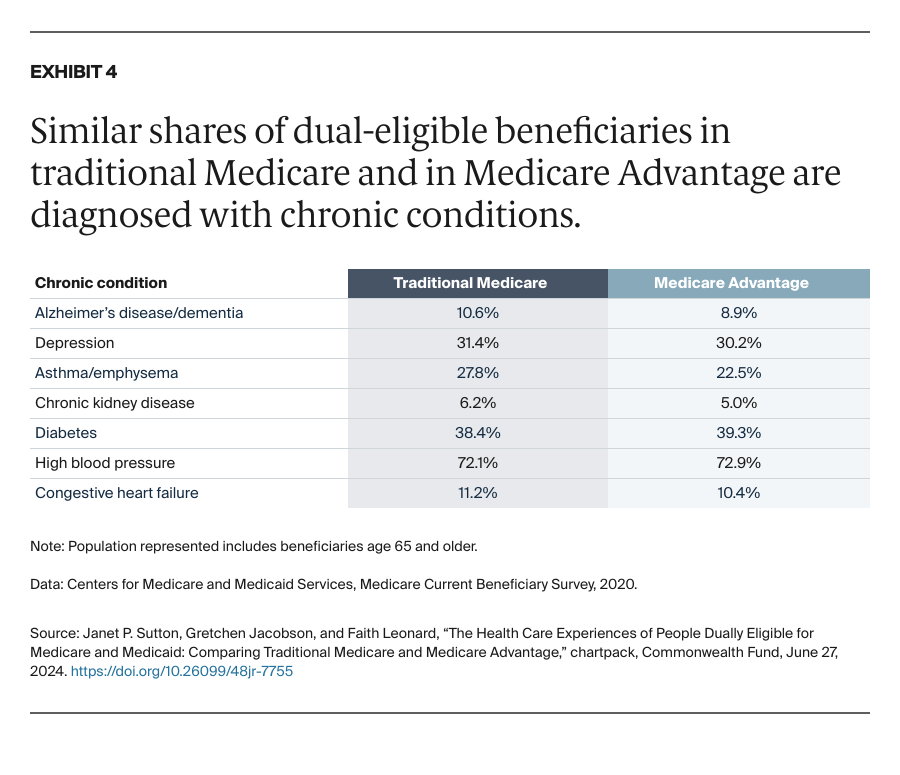
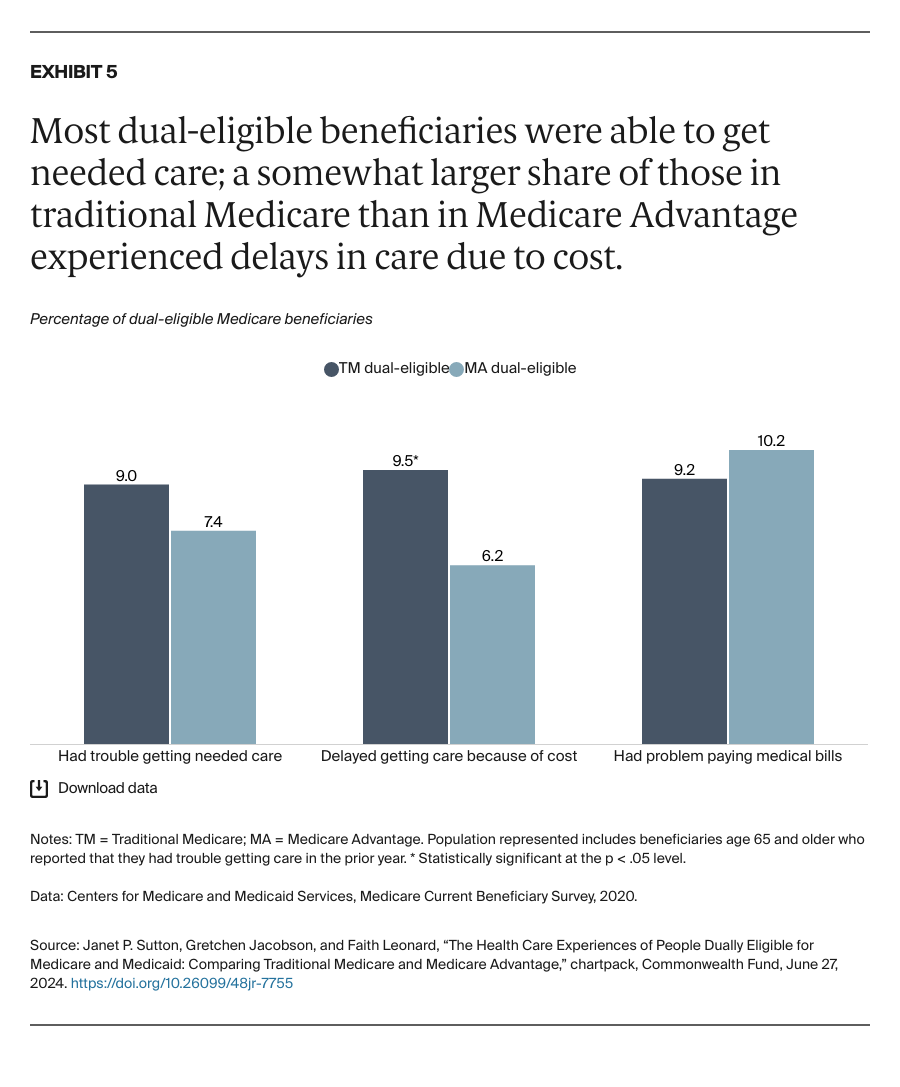
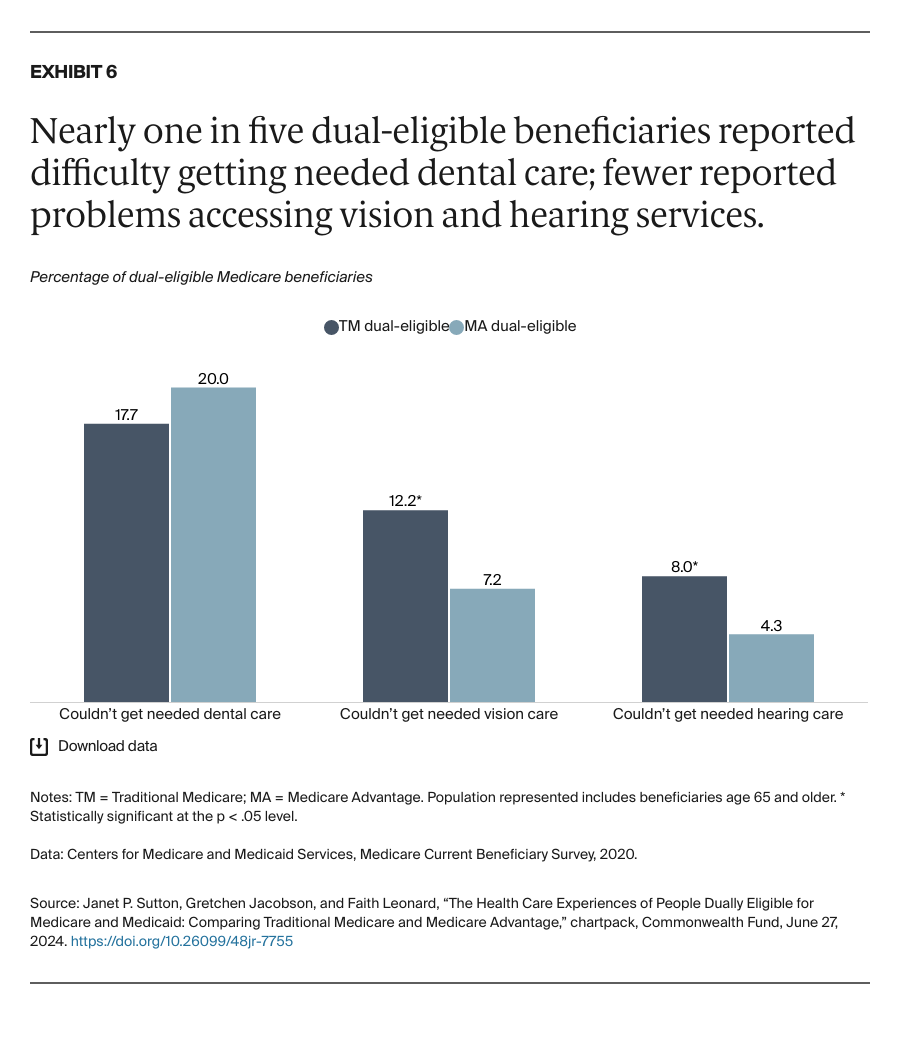
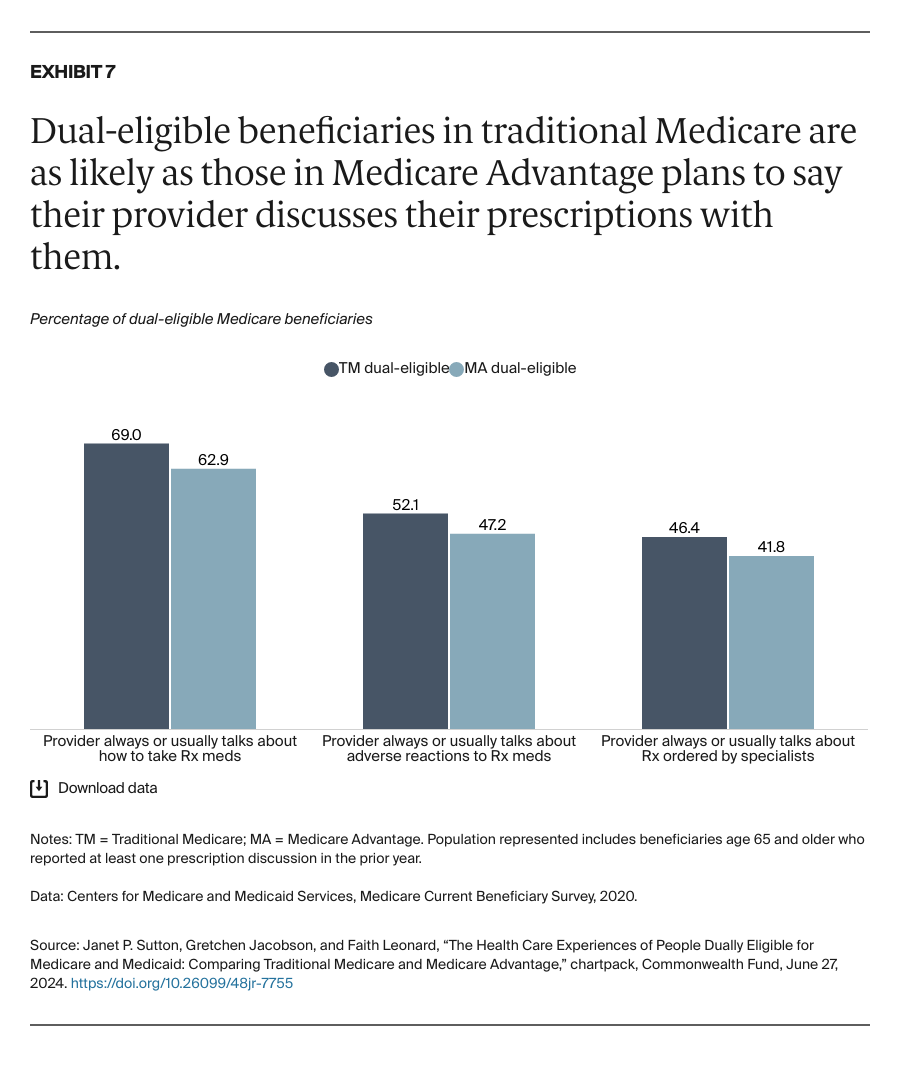
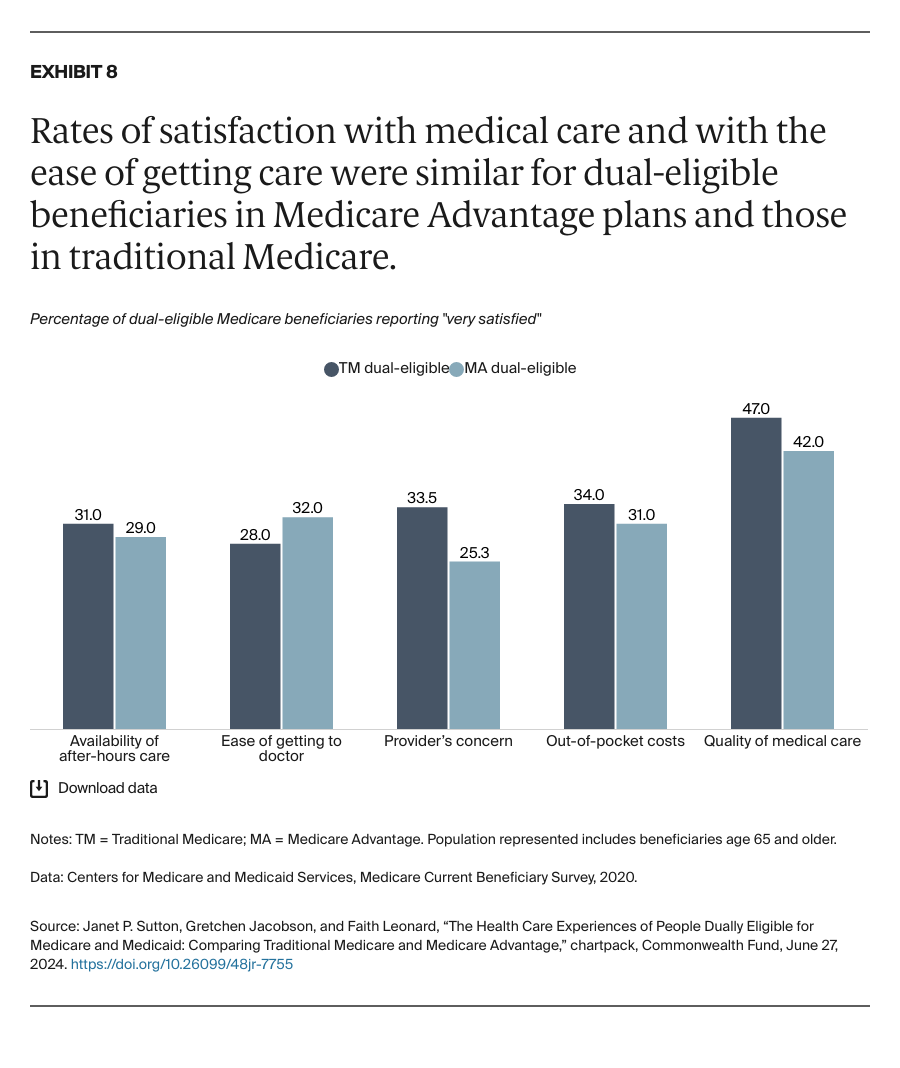
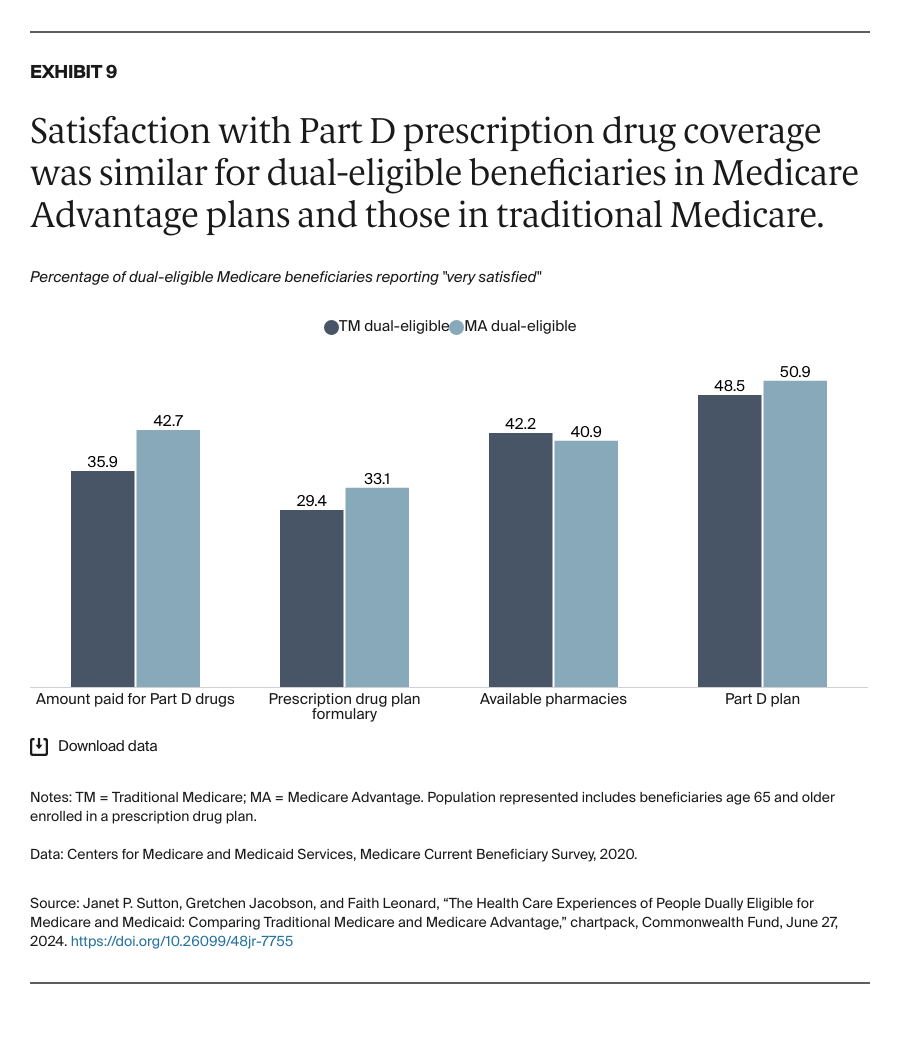
People enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid coverage are known as dual-eligible beneficiaries. They qualify for Medicare because they're at least 65 years old or because they're under age 65 and have a qualifying disability or medical condition. They qualify for Medicaid because they have low income and few resources.
In 2024, about 12.8 million Americans are dual-eligible beneficiaries. Typically, they have more complex health care needs than the average Medicare enrollee. The charts that follow compare the health care experiences of dual-eligible beneficiaries enrolled in the traditional Medicare program with those in Medicare Advantage, which provides Medicare benefits through private insurance plans.